NVIDIA GTC Europe 2017
A short review about the GPU Technology Conference (GTC) Europe in Munich from 11th to 13th October #GTC17EU. The all reference about this review is at the bottom on this page.
Max-Joseph-Straße 5, 80333 München, Germany
Keynote
Jensen Huang, the NVIDIA CEO has introduced the Keynote of the news about the new products from Virtual reality, software ecosystem, Automotive and Robotics.
The featured key for this conference is the Artificial Intelligence (A.I.) and the improving of all performance in every NVIDIA products.
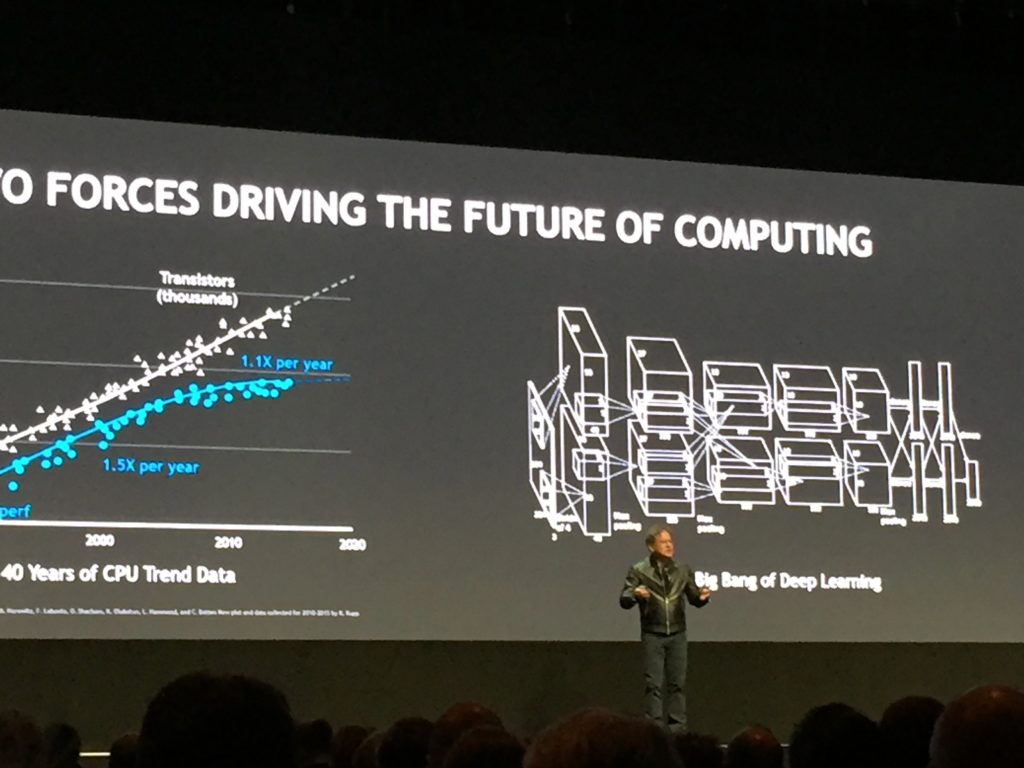
As every key note the CEO has shown the future of the computing (in figure) with the destruction of Moore’s law according to which the number of components on one integrated circuit doubles every 12 to 24 months, while cost being nearly constant. Jensen has been predicted note that in 10 to 15 years the power of GPUs will top that of CPUs by the factor of 1.000.
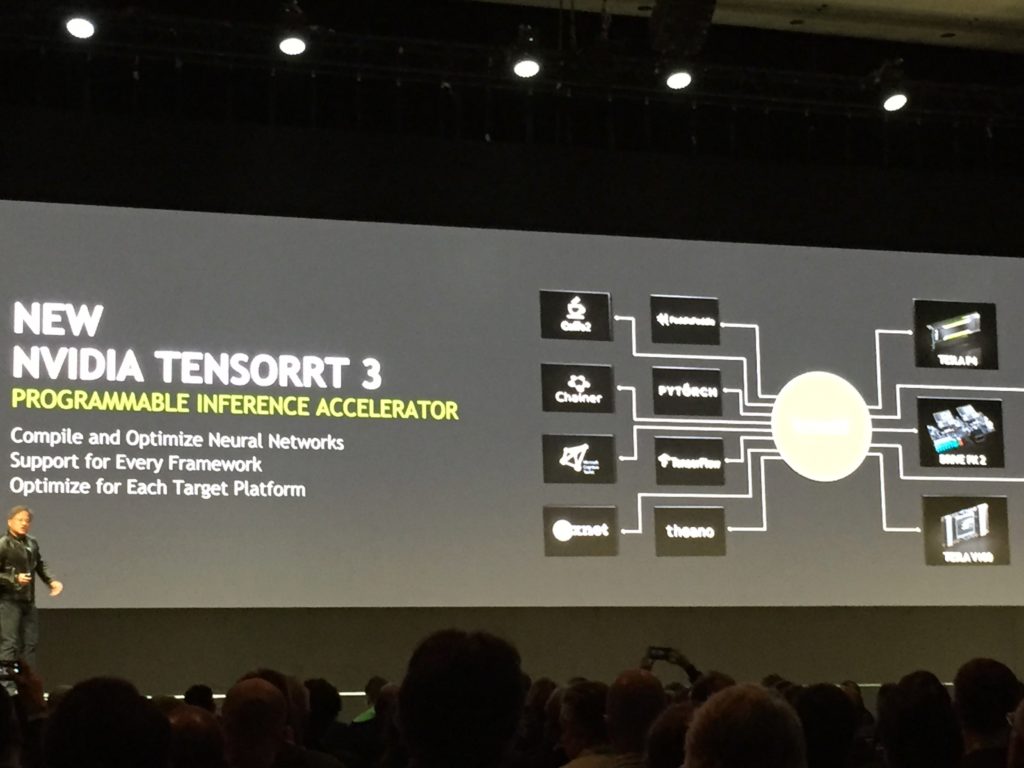
After the introduction, the key note has been divided in four arguments about the new “TensorRT 3” a new version of the famous system for deep learning from this corporation. Jensen has shown with a kind game “before-after” the difference of speed up and reduction of the space for the new data centre.


Hindsight the interesting news are on the collaborative system called “Holodeck” (in develop), the new DRIVE PX code Pegasus and finally the new first autonomous machine processor for robotic systems called “Xavier”. These last arguments are being explained in detail.
Holodeck
It is a photorealistic Virtual Reality (VR) environment for collaborative design and virtual prototyping, where high-resolution 3D models can be brought into a real-time VR space. The idea is soliciting community feedback and input via early access as they continue to develop Holodeck as a product.

Holodeck is powered by the Unreal Engine where multiple users currently connect to the same session. Every session will be similar to hosting a video game, whereby one person acts as the host and all other players will require the assets in advance to connect. This may require some fine tuning, especially when some high-resolution models will run into the gigabytes of data and need to be shared with all parties intending to connect in advance.
Holodeck has an early access to the system workflow, in automotive industry has available to show the CAD model example natively loaded with Maya or 3ds Max where the materials, geometry, textures are exported to a specific file format, and then imported to Holodeck using a plugin. Other CAD environments will be supported over time due to the use of Holodeck APIs. On that note, NVIDIA commented that Holodeck is intended for users with pre-existing CAD expertise.
PhysX has a technology that described the interaction inside the VR scene with the physics, during the show, the CEO, has been show how has possible to use the physics in a collaborative environment system.

The required hardware for the Early Access of Holodeck will be require a GeForce GTX 1080 Ti, Titan Xp, or Quadro P6000, in addition to an HMD, this access will be limited in a fixed number of passes and will be opened to all later.
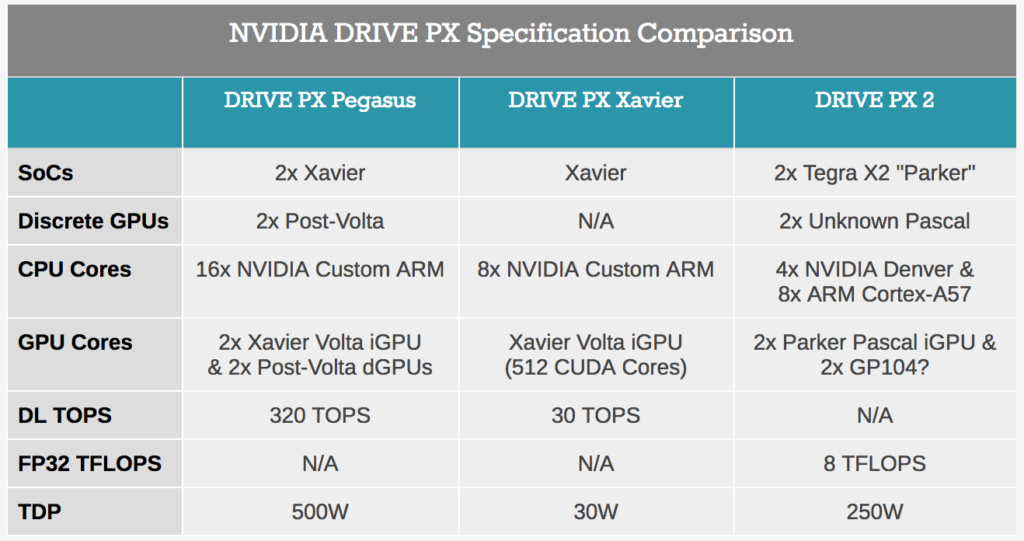
Drive PX (code name: Pegasus)
Heart of the keynote Jensen introduce the news about automotive with the new Drive PX codenamed “Pegasus” with 320 TOPS for 500W. It’s designed to enable Level 5 driverless vehicles (e.g. robotaxis that can operate without any human intervention) to go into production in future, but we do not have detail about the date.
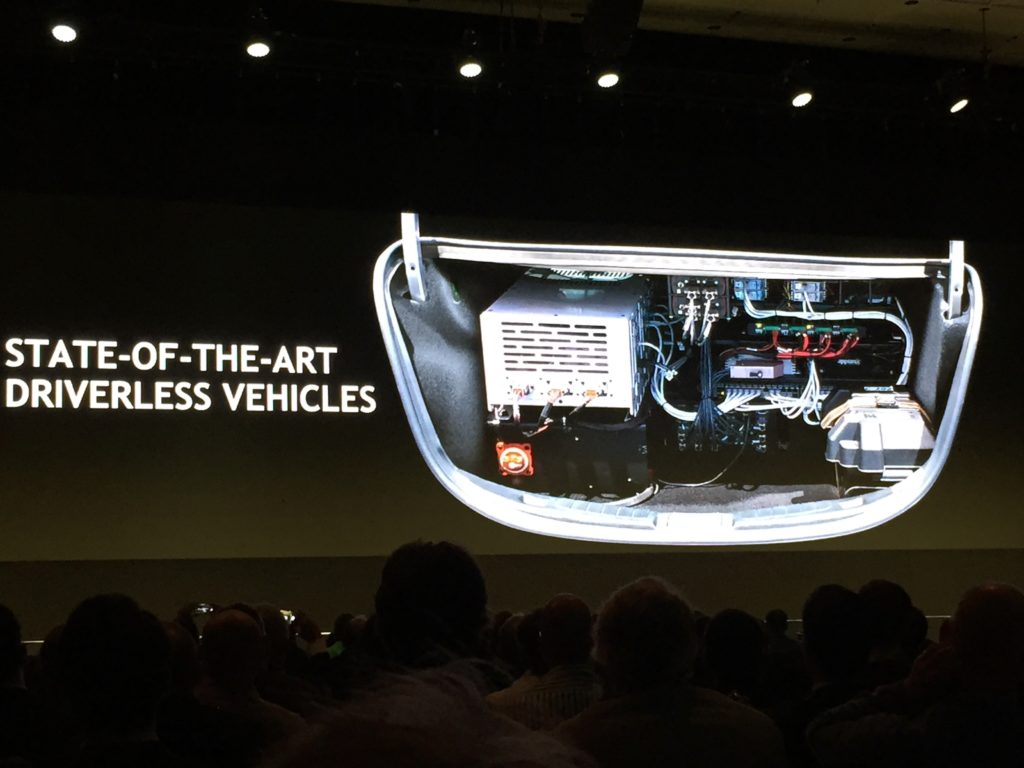

During the automotive news Jensen has shown a new software development kit called NVIDIA DRIVE IX, which stands for intelligent experience. for the company’s AI co-pilot technologies. DRIVE IX enables AI to understand sensor data from cameras and microphones inside and outside the car to enable new capabilities, such as facial identification to unlock the car, gaze-tracking to monitor driver distraction and drowsiness, among others.
The Drive PX Pegasus is very much a forward-looking product. While NVIDIA is announcing it today, they won’t even have dev kits available until later next year, and any kind of commercial release is farther off still. Consequently, the specifications for Drive PX Pegasus are equally forward looking: the board features two unannounced post-Volta next-generation discrete GPUs, which will be doing most of the heavy lifting. To put this in context, NVIDIA has only just started shipping Big Volta (GV100) for compute products, and smaller scale Volta GPUs are not expected until 2018, so we’re looking at something quite far into the future. Meanwhile, rounding out the package and serving as the hearts of the Pegasus will be a pair of NVIDIA’s upcoming Xavier SoCs, which combine an integrated Volta GPU (complete with tensor cores) with an unnamed octa-core ARM CPU design.


In terms of availability, PX Pegasus development kits will be available for select automotive partners in the second half of 2018. However, it was not clear if this sampling involved full dev kits with prototype-grade silicon, or an emulation-style system with current-generation hardware to kickstart development. Otherwise, given the long testing and validation cycles in the automotive industry, Drive PX Pegasus may not show up in vehicles for several more years. Last year NVIDIA announced their Level 4 autonomous hardware, but we are only now seeing Level 3 vehicles being showcased in early development for deployment, emphasizing that embedded time scales are much longer than consumer hardware. NVIDIA has stated that their automotive platforms are designed for typical embedded-level longevity, in this case their ‘minimum’ is a decade of use.
Finally, Jensen has shown how many start-ups works with the NVIDIA Automotive ecosystem and as over 145. A new record in terms of diffusion and use for the DRIVE PX system.

Other the Xavier board NVIDIA has announced a collaboration with Baidu and TomTom with a new map system applied for automotive system.
Xavier (robotics)
Project XAVIER is announced as the world’s first autonomous machine processor (30 TOPS at 30W). Here, machines are teaching machines to perform a specific task and finally computer programs will be able to program other computer programs. The questions who will be able to control this process however is still open.


In the keynote, Jen-Hsun additionally revealed updated sampling dates for the new SoC, stating that Xavier would begin in Q1 2018 for select early development partners and Q3/Q4 2018 for the second wave of partners. This timeline actually represents a delay from the originally announced Q4 2017 sampling schedule, and in turn suggests that volume shipments are likely to be in 2019 rather than 2018.
Robotics
In the GTC I have showed my robot in the NVIDIA autonomous machines area. With me has been shown different type of robots, principally wheeled, and humanoid and one drone.
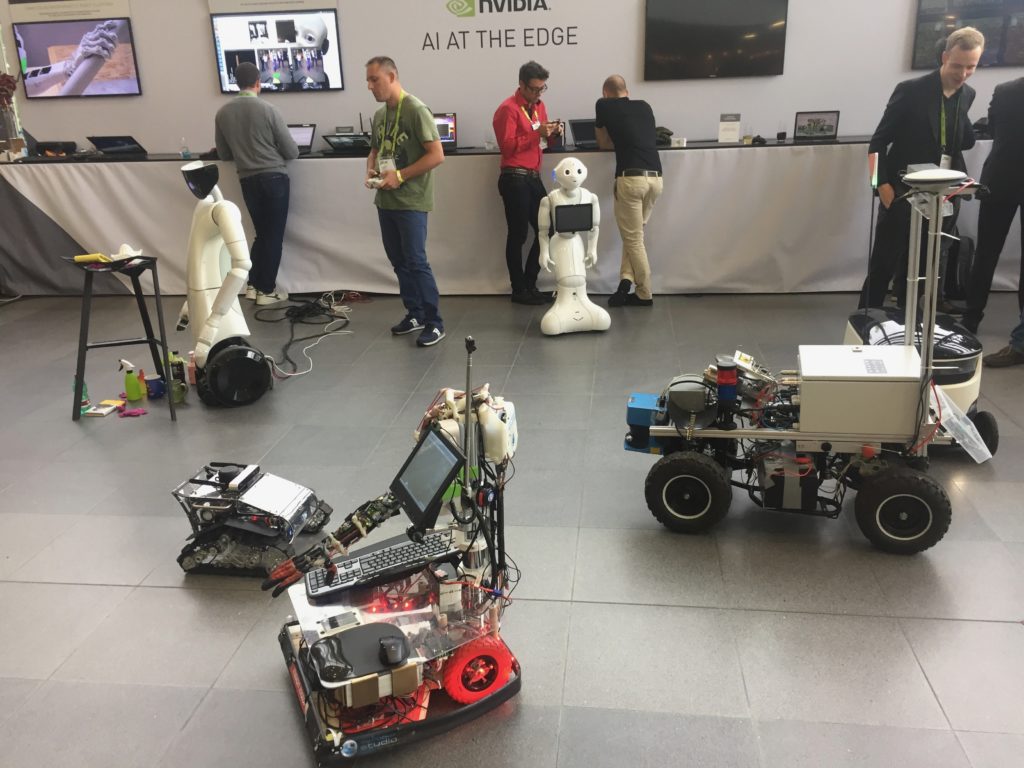

The Drone is a IFM (Intelligent Flying Machine) this can fly autonomously in factory for logistic and management of industry. It can be flight to max six meters for second. This drone during the conference has no flight.
In the second place has shown the autonomous car from Starship to autonomous delivery. More company works with this system example the fast food company in USA.
The humanoid robots shown are Pepper from Aldebaran, now Softbank and R1 from Italian Institute of Technology (IIT). There a robot for interaction and has been able to interact with the people and can be recognize with the Jetson TX2 on board in real-time.
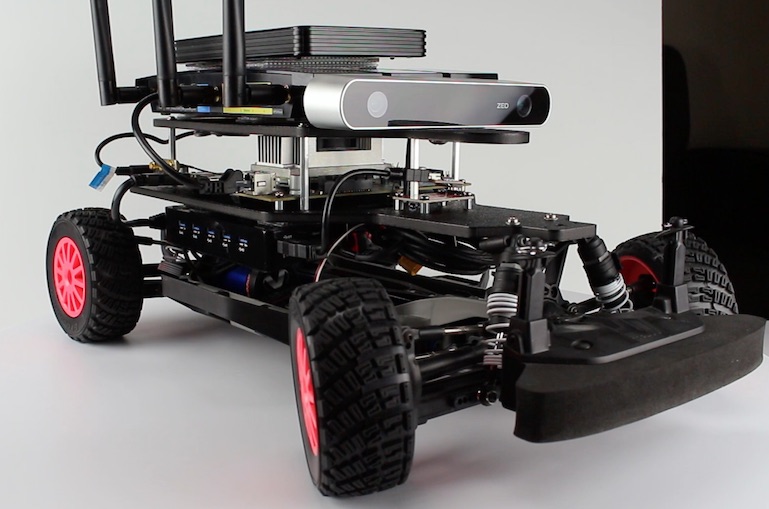
Finally, a race car model with a Jetson TX2, ZED Stereolabs camera and a Lidar. This robot has totally integrated in ROS and can be move really fast and recognize the obstacle and can be steering autonomously.
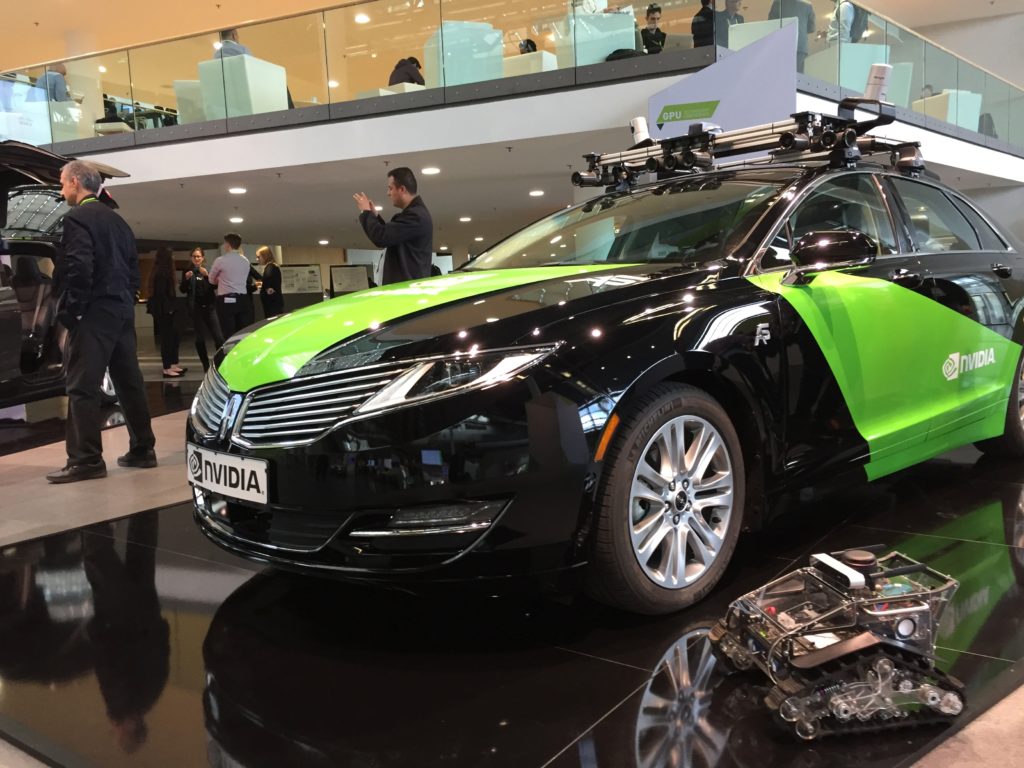
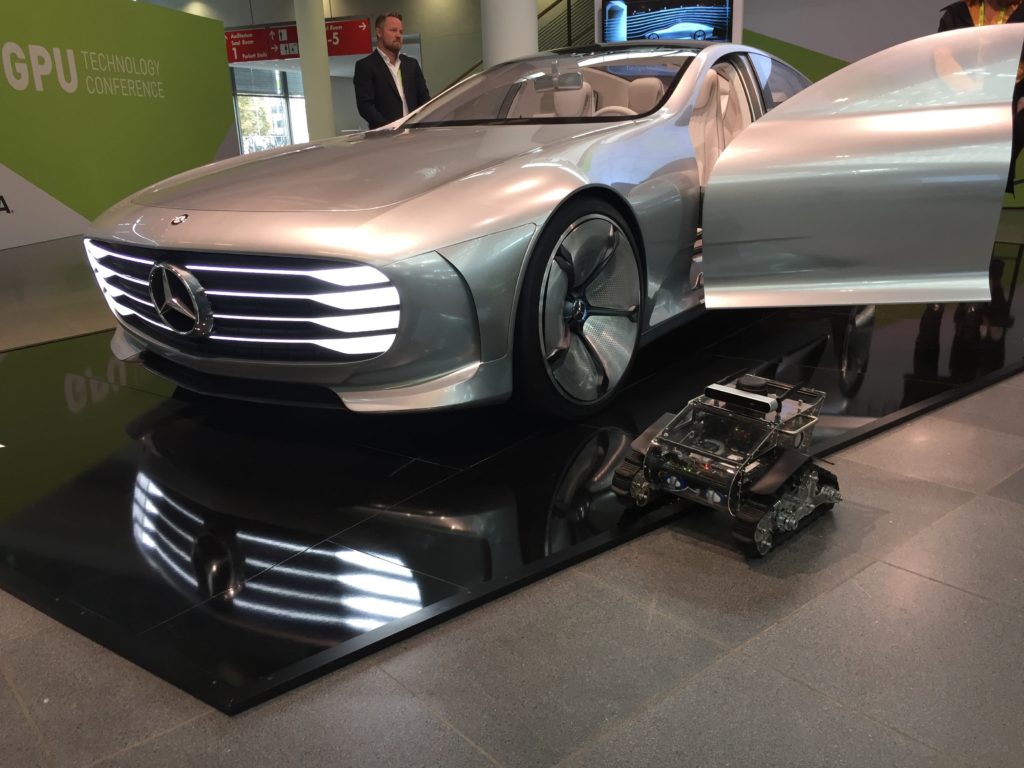
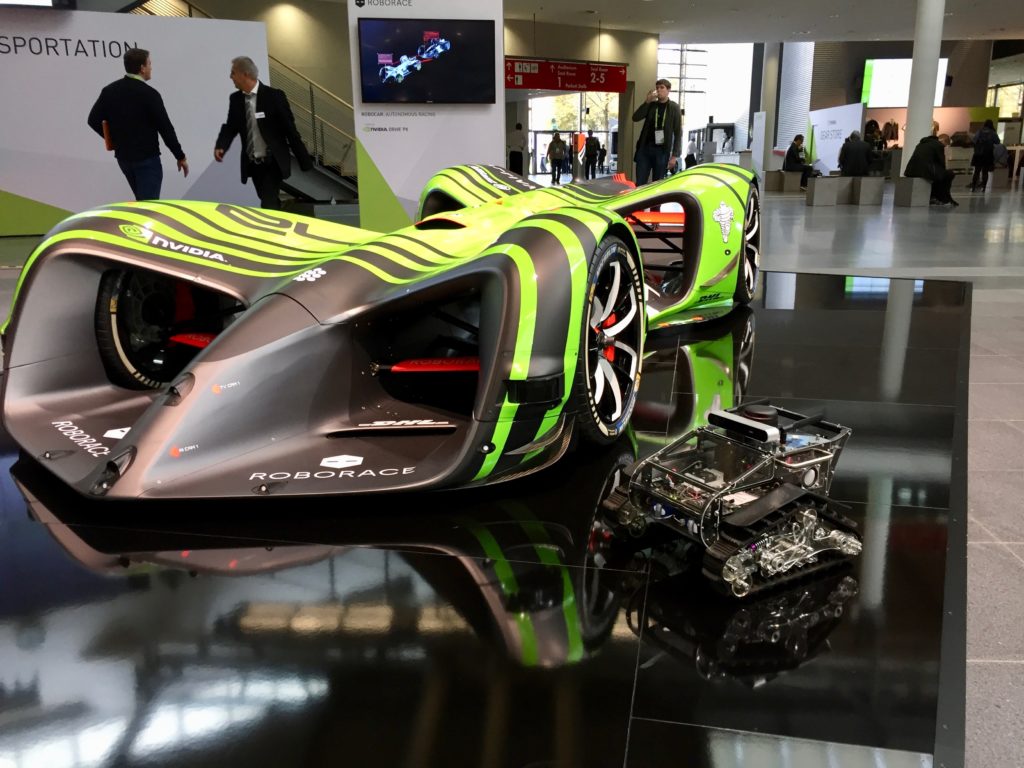



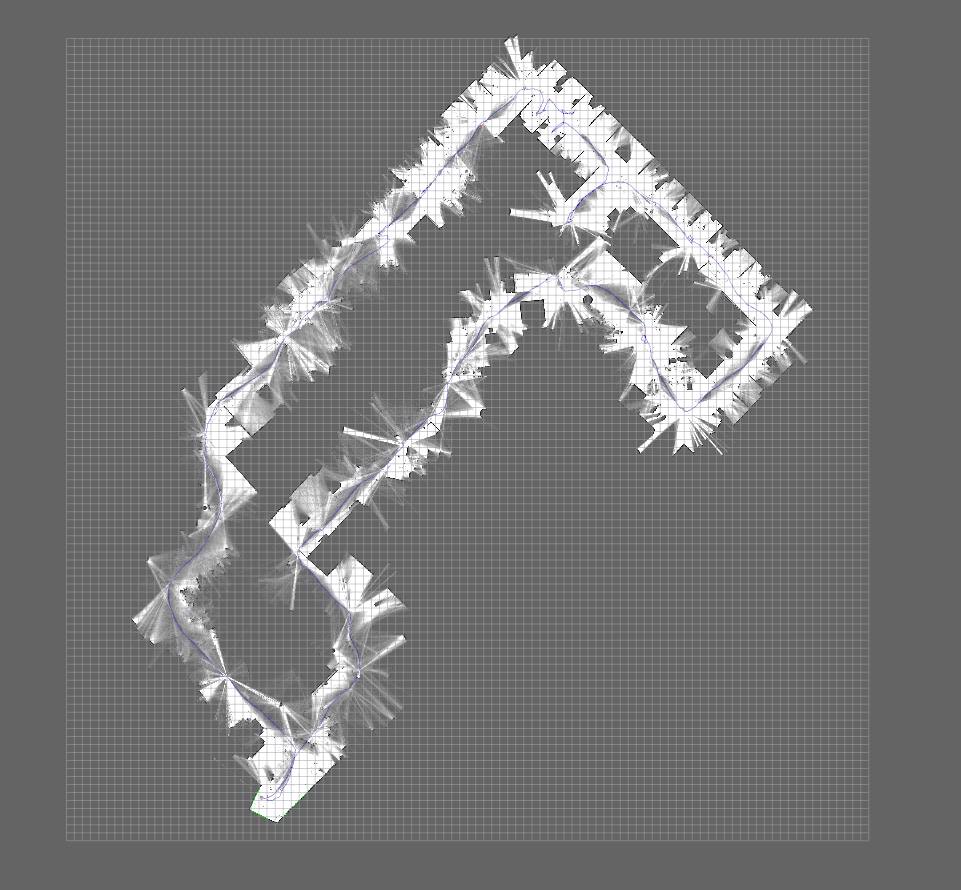
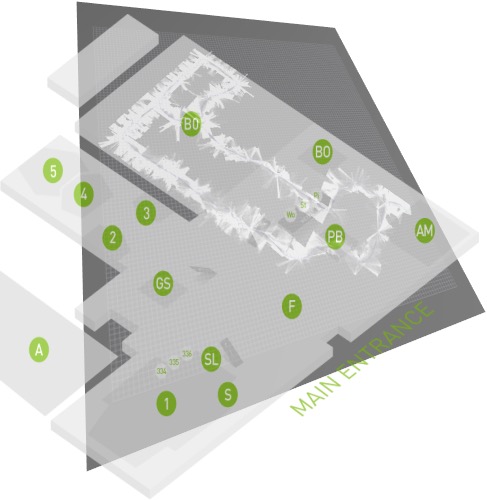
Panther map building
During the conference Panther made a map for all booths, below a gallery
Reference
- (ENG) Holodeck
- (ENG) Pegasus 2017
- (ENG) NVIDIA Xavier
- (ENG) Impression GTC Europe 2017
- (ITA) Wired la carica delle macchine autonome
- (ITA) HW Upgrade - auto autonome